1. 자바스크립트와 자바의 차이점 / 객체, 객체의 생성 방법
자바스크립트의 함수 (function) : 내장 객체인 Function 생성자로 생성된 객체
- 자바의 method와는 다름
- Function 자체가 또 하나의 객체이기도 함
자바스크립트의 method : Function 이 객체의 Property가 될 때, 메소드라고 부름
//Func은 함수, 내부의 func은 메소드
function Func() {
this.func = function () {}
}함수는 객체이므로, 프로퍼티와 메소드를 가질 수 있다.
var workout = function () {};
console.log(workout instanceof Function); // trueworkout은 Function 객체임을 확인 할 수 있음
Function 객체는 유일하게 호출이 가능하다 : 자바스크립트엔 많은 객체가 있지만, Function 객체와 다른 객체와의 차이점은 유일하게 호출이 가능하다는 점이다.
=> 호출이 가능하다는 점 때문에 prototype을 가질 수 있다. (함수만이 유일하게 프로토타입을 가진다.)
자바스크립트에서 객체를 생성하는데 함수를 new 와 함께 사용 : 이때, 함수는 "생성자"의 역할을 함
- 생성자 역할을 할 땐 대문자로 시작해야함 (규약)
function User() {}
var user = new User();
함수를 생성하는 다양한 방법
1. 함수선언 (function declaration) : function User() {}
2. 함수표현식 (function expression) : var user = function () {}
3. new Function() 키워드를 사용한 방법 : 성능과 가독성이 떨어져 권장하지 않음
객체와 클래스
자바스크립트에서 객체를 생성하는 몇가지 방법
1. Object() 생성자
2. 객체 리터럴
3. 생성자 함수
4. Object.create();
5. 생성함수
6. ES6의 클래스
1. Object() 생성자
//new 활용해서 Object 생성자 호출
var user = new Object();
user.name = 'Sunny';
user.interests = ['Traveling', 'Swimming'];
user.greeting = function () {
console.log('Hi I\'m ' + this.name + '. ');
};
user.greeting(); //Hi I'm Sunny.객체의 Wrapper를 생성하는 방법 (타입을 감싸는, 타입을 받을 수 있는 객체).
간결하지 않아서 이 방법은 권장하지 않음
2. 객체리터럴
var user = {
name: 'Sunny',
interests: ['Traveling', 'Swimming'],
greeting: function () {
console.log('Hi I'\m ' + this.name + '. ');
}
}
user.greeting(); //Hi I'm Sunny.new Object()를 이용하는 것보단 권장. ES5 객체 리터럴에서 getter, setter 접근자 사용하는 것을 지원.
var user = {
get role() {
return 'Engineer';
}
}
console.log(user.role); //Engineer이렇게 사용 가능. 이는 setter에 대한 정의가 없기 때문에
user.role = 'new Enginner'; 과 같이 사용 불가능
3. 생성자함수를 이용하는 방법
function User(name, interests) {//생성자 함수의 선언
this.name = name;
this.interests = interests;
this.greeting = function () {
console.log('Hi, I\'m ' + this.name + '. ');
}
}
var user = new User('Sunny', ['Traveling','Swimming']);
user.greeting(); //Hi, I'm Sunny.이는 자바와 매우 유사한 방법. 자바스크립트에서는 호출할 때 인자를 생략가능 (관대, 인자 전달은 안됨). 유효는 하나 권장하지 않음
var user = new User;
console.log(user.name); //undefined
4. Object.create()를 이용하는 방법
function User(name, interests) {
this.name = name;
this.interests = interests;
this.greeting = function () {
console.log('Hi, I\'m ' + this.name + '. ');
}
}
var user = Object.create(User.prototype, Object.create(User.prototype), {
name : {value:'Sunny'},
interests : {value:['Traveling', 'Swimming']}
});
user.greeting() //uncaught TypeError : user.greeting() is not a functionuser 객체에 Object.create를 이용해서 만든 객체를 전달함.
프로토타입은 User 생성자 함수의 것을 전달하고 내부 프로퍼티는 2번 째 인자로 전달한다는 뜻이다.
이 때 greeting 함수가 user의 객체의 것이 아닌 이유는 Object.create() 메소드는 새로운 객체를 만들어 전달했기 때문이다.
프로토타입을 전달한다는 이 특징을 이용해서 자바스크립트의 상속에 사용하기도 함!
이는 나중에 설명
console.log(Object.create(User.prototype));
console.log(Object.create(User.prototype), {
name : {value:'Sunny'},
interests : {value:['Traveling', 'Swimming']}
});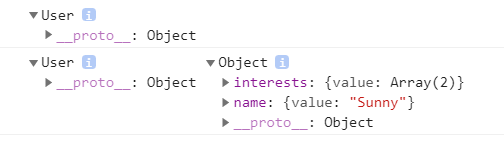
보면 알겠지만, 위에는 User 생성자 함수의 프로토타입만 전달하고, 아래에는 프로토타입과 더불어 프로퍼티를 같이 전달한다.
greeting 함수를 전달하는 두가지 방법
방법1.
var user = Object.create(User.prototype, {
name: {value:'Sunny'},
interests: {value: ['Traveling']},
greeting: {value: function() {
console.log('Hi, I\'m ' + this.name + '. ');
}
}
});
=> 2번째 인자로 greeting까지 전달
방법2.
User.prototype.greeting = function () {
console.log('Hi, I\'m ' + this.name + '. ');
}=> 프로토타입으로 추가해줌
5. 생성함수를 사용 : 팩토리 메소드 사용 (원하는 객체를 직접 반환하지 않고 외부에서 반환)
//객체 자체를 반환해주는 생성함수 이용
function createUser(name, interests) {
var user = {};
user.name = name;
user.interests = interests;
user.greeting = function () {
console.log('Hi, I\'m ' + this.name + '. ');
}
return user;
}
//매개변수를 이용해서 생성함수 호출
var user = createUser('Sunny', ['Traveling','Swimming']);
user.greeting(); // Hi, I'm Sunny.
6. ES6의 클래스 사용
//User 클래스 생성
class User {
//User 생성자 함수와 상응
constructor (name, interests) {
this.name = name;
this.interests = interests;
}
//User.prototype.greeting 과 같다
greeting() {
console.log('Hi, I\'m ' + this.name + '. ');
}
}
let user = new User('Sunny', ['Traveling', 'Swimming']);
user.greeting(); // Hi, I'm Sunny.
클래스 표현식 사용
let user = class {
constructor (name, interests) {
this.name = name;
this.interests = interests;
}
greeting() {
console.log('Hi, I\'m ' + this.name + '. ');
}
}
클래스를 사용해서 객체를 생성하는 방법은 자바와 매우 유사하나, 자바와 달리 private class나 static 클래스가 없다.
'모던 웹 애플리케이션 개발 > 자바스크립트(JavaScript)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 4. 자바스크립트 ES6 에서 추가된 문법 (0) | 2021.02.02 |
|---|---|
| 3. 자바스크립트의 실행컨텍스트(this), 호이스팅 (0) | 2021.01.31 |
| 2. 자바스크립트와 자바의 차이점 / 프로퍼티, 프로토타입, 변수 스코프 (0) | 2021.01.25 |
댓글
이 글 공유하기
다른 글
-
4. 자바스크립트 ES6 에서 추가된 문법
4. 자바스크립트 ES6 에서 추가된 문법
2021.02.02 -
3. 자바스크립트의 실행컨텍스트(this), 호이스팅
3. 자바스크립트의 실행컨텍스트(this), 호이스팅
2021.01.31 -
2. 자바스크립트와 자바의 차이점 / 프로퍼티, 프로토타입, 변수 스코프
2. 자바스크립트와 자바의 차이점 / 프로퍼티, 프로토타입, 변수 스코프
2021.01.25